[ Instrument R & D of Instrument Network ] On April 28, the team of Zhao Fangqing of the Beijing Academy of Life Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences published a research paper entitled CircAtlas: an integrated resource of one million highly accurate circular RNAs from 1070 vertebrate transcriptomes in the international journal Genome Biology. The research is based on the existing massive transcriptome data and uses multi-dimensional data intelligent integrated analysis methods to successfully analyze the expression characteristics and evolution laws of circular transcripts across species, multiple organizations, and large samples. The overall picture of RNA and the generation mechanism provide strong data support.
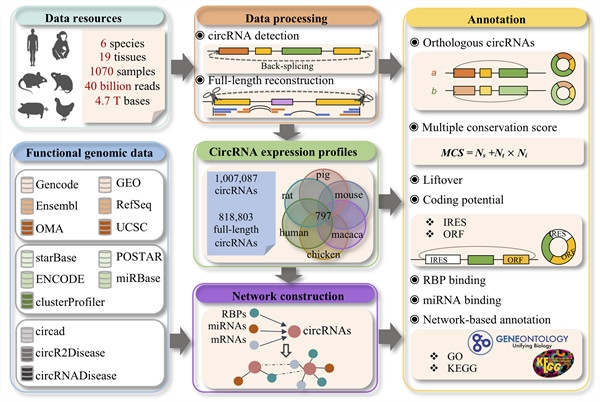
In recent years, circular RNA has been continuously discovered and expanded as a new type of endogenous non-coding RNA in the regulation of biological systems and disease development. The rapid development and wide application of high-throughput sequencing technology has brought circular RNA research into the era of big data, making it quickly become one of the hot spots in the field of RNA research. The massive accumulation of circular RNA transcriptome data has brought new opportunities and challenges to researchers: how to efficiently screen and obtain circular RNA molecules with important biological functions from the ocean of transcriptome data. The increasing variety of species information opens a new breakthrough for the comprehensive interpretation of the complex circular RNA transcription regulation process: the evolutionary conservative analysis based on multiple species will help screen out potential functional circular transcripts, and the integrated analysis of multi-omics data Then the expression regulation process of circular RNA can be analyzed from different levels.
The researchers obtained 19 tissue types covering 6 species (human, monkey, mouse, rat, pig, and chicken) by integrating their own and public transcriptome data, a total of 1070 transcriptome data sets, and constructed the current coverage CircAltas (http://circatlas.biols.ac.cn), a circular RNA integrated data resource platform with wide species and complete data. The platform contains more than 1 million high-quality circular RNA molecules, of which> 80% have full-length transcript sequences. In addition, by integrating functional omics data and annotation information, it provides important data resources and technical support for circular RNA data mining and functional research.
On the basis of the above data, they further proposed a new conservative circular RNA recognition method and a conservative multi-level evaluation mechanism. By combining the characteristics of global alignment and local alignment of reverse splicing sites, more than 120,000 conserved circular RNAs were screened, and the conservativeness was further scored by combining the expression consistency between species, tissues and individuals (Multiple Conservation Score), which intuitively reflects the conservation and evolution of circular transcripts at different levels, is of great significance for the screening of functional circular RNA molecules. In addition, the researchers combined the conservation and expression information to rename the collected circular RNA, and provided the function of name query and conversion between multiple circular RNA databases to clarify the naming confusion in the field of circular RNA. In addition, using the full-length sequence of the reconstructed circular RNA, the team first analyzed its possible ORF and IRES sequences on a large scale to predict its potential for translation into proteins. Further combined with CLIP and other multi-omics data, a circular RNA and mRNA, miRNA and RBP expression regulation network is constructed, and the annotation information of many regulatory elements in the network is combined to predict the function of the circular RNA. This research provides an important analysis tool for the function mining and annotation of circular RNA.
The work was completed by Wu Wanying, a PhD student in Zhao Fangqing's research group, and Ji Peifeng, an assistant researcher, and received financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Key Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology and the Chinese Academy of Sciences. In the previous work, Zhao Fangqing team established a series of methods and tools such as circular RNA recognition and quality control, transcript assembly, alternative splicing recognition and quantification. 2020), Briefings in Bioinformatics (2017), Trends in Genetics (2018), Genome Medicine (2019), Cell Reports (2019) and Bioinformatics (2020). These studies have enriched people's understanding of the expression and function of circular RNA and laid a methodological foundation for in-depth understanding of this new type of non-coding RNA molecules.

As a leading enterprise in the galvanized & pre-painted industry in china. Shandong Xinghan Materail Corporation with an annual output of 1 million tons of picking coils. 1 million tons of cold roll. 800,000 tons of hot-dipped galvanized and galvalume steel sheets. 450,000 tons of thicker galvanized steeel sheets.300,000 tons of pre-painted steel sheets. occupies a stable leading position in the industry.
The company has 2 PPGI/PPGL production lines, taking GI or aluzinc sheet as its base material. adopt advanced painting technology, Main thickness rang is 0.15mm to 1.0mm and width 750 to 1250mm.

Prepainted Galvalume Steel Coil
Ppgi And Ppgl,Pre Painted Steel Sheet,Prepainted Galvalume Coil,Prepainted Galvalume Steel Coil
SHANDONG XINGHAN MATERIAL CORPORATION , https://www.xinghansteel.com

